Host on GitHub Pages
Prerequisites
- Create a GitHub account
- Install Git
- Create a Hugo site and test it locally with
hugo server.
Types of sites
There are three types of GitHub Pages sites: project, user, and organization. Project sites are connected to a specific project hosted on GitHub. User and organization sites are connected to a specific account on GitHub.com.
Procedure
- Step 1
- Create a GitHub repository.
- Step 2
- Push your local repository to GitHub.
- Step 3
- Visit your GitHub repository. From the main menu choose Settings > Pages. In the center of your screen you will see this:
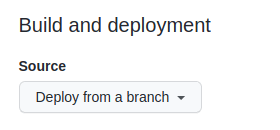
- Step 4
- Change the Source to
GitHub Actions. The change is immediate; you do not have to press a Save button.
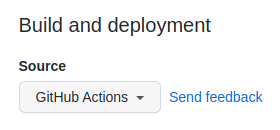
- Step 5
- Create an empty file in your local repository.
.github/workflows/hugo.yaml
- Step 6
- Copy and paste the YAML below into the file you created. Change the branch name and Hugo version as needed.
.github/workflows/hugo.yaml
# Sample workflow for building and deploying a Hugo site to GitHub Pages
name: Deploy Hugo site to Pages
on:
# Runs on pushes targeting the default branch
push:
branches:
- main
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# Sets permissions of the GITHUB_TOKEN to allow deployment to GitHub Pages
permissions:
contents: read
pages: write
id-token: write
# Allow only one concurrent deployment, skipping runs queued between the run in-progress and latest queued.
# However, do NOT cancel in-progress runs as we want to allow these production deployments to complete.
concurrency:
group: "pages"
cancel-in-progress: false
# Default to bash
defaults:
run:
shell: bash
jobs:
# Build job
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
HUGO_VERSION: 0.126.0
steps:
- name: Install Hugo CLI
run: |
wget -O ${{ runner.temp }}/hugo.deb https://github.com/gohugoio/hugo/releases/download/v${HUGO_VERSION}/hugo_extended_${HUGO_VERSION}_linux-amd64.deb \
&& sudo dpkg -i ${{ runner.temp }}/hugo.deb
- name: Install Dart Sass
run: sudo snap install dart-sass
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
submodules: recursive
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Setup Pages
id: pages
uses: actions/configure-pages@v4
- name: Install Node.js dependencies
run: "[[ -f package-lock.json || -f npm-shrinkwrap.json ]] && npm ci || true"
- name: Build with Hugo
env:
# For maximum backward compatibility with Hugo modules
HUGO_ENVIRONMENT: production
HUGO_ENV: production
TZ: America/Los_Angeles
run: |
hugo \
--gc \
--minify \
--baseURL "${{ steps.pages.outputs.base_url }}/"
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v3
with:
path: ./public
# Deployment job
deploy:
environment:
name: github-pages
url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: build
steps:
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
id: deployment
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v4- Step 7
- Commit the change to your local repository with a commit message of something like “Add workflow”, and push to GitHub.
- Step 8
- From GitHub’s main menu, choose Actions. You will see something like this:
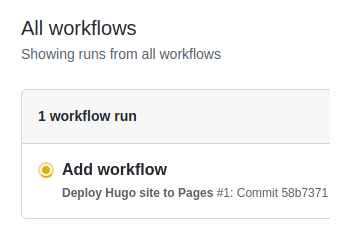
- Step 9
- When GitHub has finished building and deploying your site, the color of the status indicator will change to green.
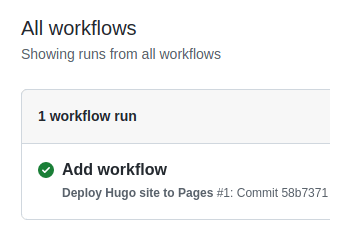
- Step 10
- Click on the commit message as shown above. You will see this:
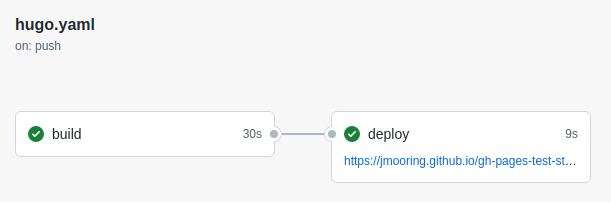
Under the deploy step, you will see a link to your live site.
In the future, whenever you push a change from your local repository, GitHub will rebuild your site and deploy the changes.
Customize the workflow
The example workflow above includes this step, which typically takes 10‑15 seconds:
- name: Install Dart Sass
run: sudo snap install dart-sass
You may remove this step if your site, themes, and modules do not transpile Sass to CSS using the Dart Sass transpiler.